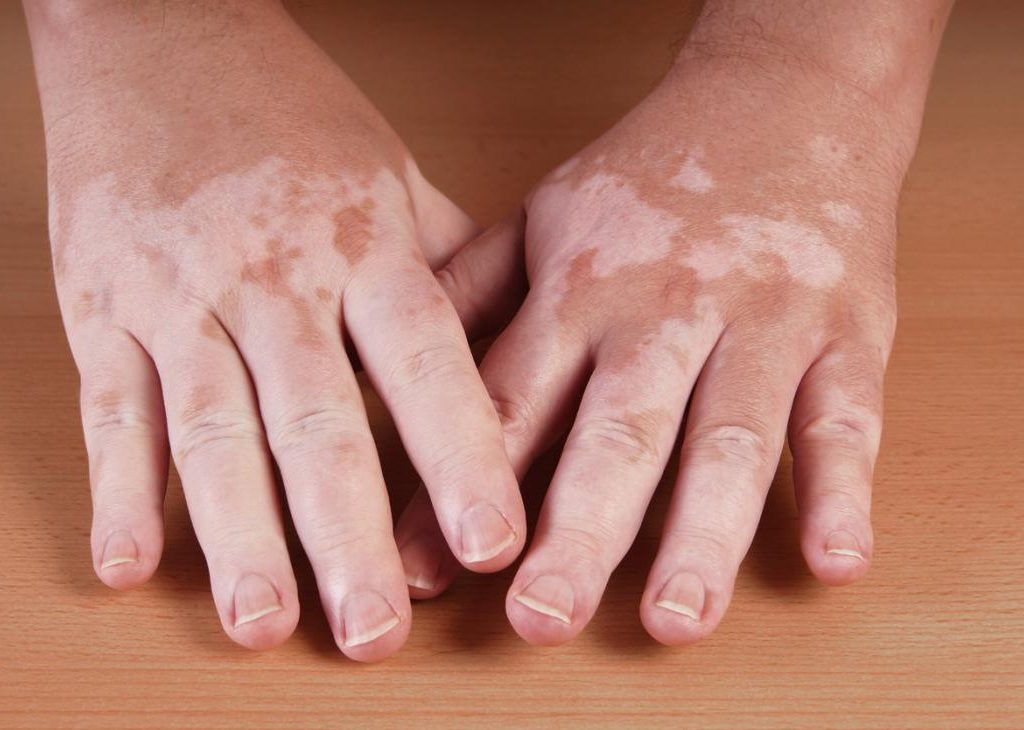
Skin brightening and whitening products are highly sought after by many who experience skin pigmentation, scarring, and several other radiative exposures from the sun, which causes uneven darkening of the skin.
However, I bet you yourself are still confused between these as they are somewhat, similar? Let’s keep on reading to find more info about the ingredients, sciences, and differences between these two.
What is Skin Brightening?

Skin brightening is to increase the brightness, radiance, and glow of the skin. Often, it involves exfoliating, moisturizing, and face rollers & laser resurfacing, resulting in brighter skin.
What is Skin Lightening?
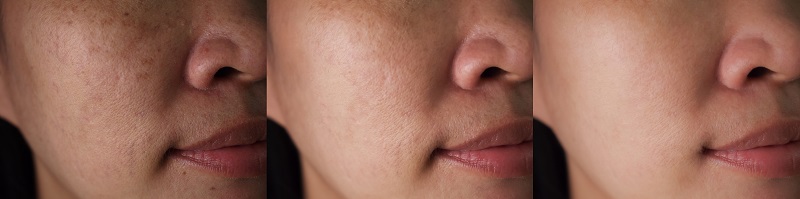
While skin lightening is to reduce pigmentation. It has to do with discolouration of the skin and evening our skin tone over time.
What Ingredients Should You Look for in Skin Brightening?
For skin brightening, you should look out for these ingredients: Vitamin C, retinol, alpha and beta hydroxy acids.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C helps to reduce the hyperpigmentation and brighten the skin by blocking melanin production. Vitamin C also blocks tyrosinase, an enzyme that is used by our body to produce melanin, making it a natural skin brightener.
Moreover, vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps to protect our skin cells from further damage from the sun and outside pollutants. There are multiple forms of vitamin C such as Magnesium ascorbyl phosphate, ascorbic acid sulfate and ascorbyl palmitate.
It is safe to use vitamin C daily in our skincare routine, however, people with sensitive skin might see redness or feel stinging from the first use.
Retinol
Retinol is one of the most powerful ingredients for hyperpigmentation. It is a form of vitamin A and particularly effective at combating hyperpigmentation by encouraging cell turnover. It exfoliates the older, darker skin and bringing healthier, newer skin cells to the surface after frequent use.
For best results, you can use retinol for several months or more. If you are new to this, I would advise for you to use it 1-2 times a week, before you start to use it regularly – as the concentrations might be too strong for you.
One thing to take note is, please avoid to use it when you are pregnant as it might cause some birth defects.
Alpha and Beta Hydroxy Acids
Have you heard of Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHA) and polyhydroxy acids (PHAs)? All these three categories are under hydroxy acids. They work similarly but each one produce different results.
In a nut shell, hydroxy acids smoothen, tighten, firm and brighten the skin. It exfoliates the skin by dissolving the cellular glue and exfoliating superficial, dead skin cells resulting in a healthy, younger skin. You can see significant improvements in your skin when you use it as directed.

What Ingredients Should You Look for in Skin Lightening?
Generally, skin lighteners contain an active ingredient or a combination of ingredients that reduces the amount of melanin in the skin where it is applied. Common skin lightening ingredients include hydroquinone, niacinamide, and kojic acid.
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a reversible chemical brightening agent which works by blocking crucial enzymes (i.e. tyrosinase) in the melanogenesis pathway on the skin. It is usually used as a skin bleaching agent to tackle skin discolouration related skin conditions. The inhibition of the enzyme tyrosinase results in a chemical reduction of melanin.
Hydroquinone has been successfully used for decades to treat conditions like melasma, helping to reduce skin pigmentation and even out the skin tone. However, since the effects are reversible, topical application is required to maintain the skin lightening effect.
Moreover, misuse or overuse of this chemical can actually cause several side effects such as dryness, irritation, and also ochronosis (which is a bluish-black discolouration caused by the accumulation of homogentisic acid, during the breakdown of tyrosine in the melanogenesis pathway).
It has been banned in some European countries due to the risk of causing cancer.
Niacinamide
One of my favourite ingredients! Niacinamide is made from niacin, which is also known as vitamin B3. Niacin can be found in most cells and are present in most metabolically active tissues, such as the brain, heart, and liver.
The human body is able to make small amounts of vitamin B3, and so, it must come hugely from food sources such as fish, red meat, and nuts.
It is used as a skin brightener mainly because of its excellent cell renewing properties. Niacinamide is widely considered as a skin brightener as it is also a tyrosinase enzyme inhibitor which works similarly to hydroquinone to reduce melanin production on the skin.
There is evidence of niacinamide being used as an anti-ageing active ingredient. It is helpful for treating excessive dryness, helps produce more collagen, and also could act as a moisturising ingredient.
However, for effective skin brightening, niacinamide needs to be dosed in cosmetics at least 4% to help lighten skin pigmentation. For best results, combine it together with other proven skin brightening ingredients, such as vitamin C and retinol.
Kojic acid
Kojic acid is a by-product of a fermentation process during the manufacturing of sake (Japanese rice wine). Studies have shown the efficacy of kojic acid in skin lightening. It is an anti-oxidant and has melanin reduction properties.
However, kojic acid is very unstable in nature and upon exposure to sunlight or oxygen, it can oxidise and lose its efficacy. Research has shown that kojic acid is not cancer-causing but can cause allergic reactions and skin irritation if used in high amounts.
How to Apply Skin Brightening or Skin Lightening Products?
While it is common and generally safe for your skin to use these skin brightening and skin lightening products or ingredients, knowing the know-how can make it more effective and less likely to cause irritation. Here are a few tips that you should know especially if you are using it for the first time:
- Start slow: When you are using acids in your skincare, start conservatively with a lower concentration, one to two times per week and then work up to see what your skin can tolerate.
- Patch test IS important! Similar to the other (new) skincare product that you’re going to use, do patch test before you use it. Apply a small amount on the arm and then on the forehead to see how your skin will respond.
- Sunscreen and hydration: As the skin brightening and skin lightening’s products expose newer and more sensitive skin cells, make sure to use sunscreen daily and generously. Don’t forget to hydrate your skin with the correct moisturizer AND drinking water as well.
- Consult your dermatologist: Some people might experience redness, irritation or peeling when you first use these products. If persistent irritation occurs, please consult a certified doctor.
The correct (and simplest) way to incorporate skin brightening and skin lightening products in your skincare is:
Cleanse > Hydrating/Exfoliating toner (AHA/BHA) > Brightening/Lightening Serum > Moisturizer > Sunscreen
Whatever your skin type, tone or condition, you can find the right one for you and with frequent use, you will find yourself a healthier and happier skin!




