What is hypopigmentation?
Hypopigmentation refers to patches of skin on your body or face that lack colour or are lighter in colour from your overall skin tone. This occurs when your skin is unable to produce enough melanin and may be caused by a variety of different genetic or environmental factors. Examples of some of the most common causes and conditions are listed down below:

(cr:medicalnewstoday)
Albinism
A rare genetic defect, albinism is caused when one’s skin is unable to produce melanin – causing their hair and skin to appear white, and their eyes to have less pigment. Because melanin serves as a means for our skin to protect us from the sun’s UV rays, albinos are more prone to sunburn and can cause burning, peeling, blisters, hard or wrinkled skin, and bumps or wounds that can develop into skin cancer and be life-threatening. Thus, it is important for them to adequately protect themselves from the sun by staying indoors and wearing sun protection.
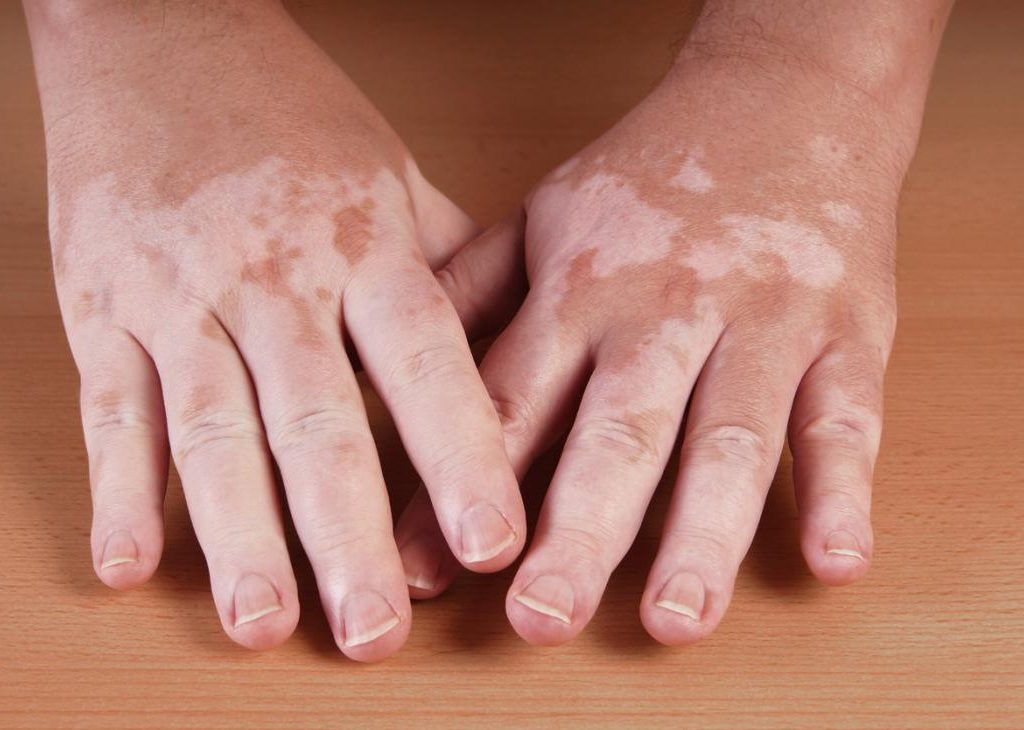
Vitiligo
Individuals with vitiligo have patches of skin that are lighter in colour. These patches may be found all over their body and/or face. The exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by an autoimmune disease that damages melanin producing cells. The lighter patches of skin are more prone to sunburn and should be protected against the sun’s UV rays.
Scars and burns, Healed blisters, Infections
The healing of infections, burns, and blisters may result in scars that are lighter in colour compared to the skin around it – resulting in hypopigmentation. These forms of discolouration may be temporary or long term, depending on the individual.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin experiences an allergic reaction/ irritation from contact with a substance. These reactions often come in the form of red, itchy rashes and is neither contagious nor life threatening. This reaction could lighten the skin – resulting in hypopigmentation.
How do I cure my hypopigmentation?
As stated by DermNet New Zealand, hypopigmentation will likely resolve itself as the affected skin cells begin to heal. The skin cells in the should be able to produce melanin again within the next skin rejuvenation cycles. If unsure or you think your hypopigmentation could be a sign of something more severe, visit a medical professional for a consultation.
Hypopigmentation is defined as the lack of melanin pigment within your skin, on various parts of your body. This results in various areas being lighter coloured as compared to the rest of your natural skintone. Thus, because The Lightening Serum targets the production of excess melanin, it might not be able to even out your skin tone entirely.
However, if you do suffer from age spots, liver spots, melasma, or dark scarring on other parts of your body, The Lightening Serum will be able to even these spots of dark pigmentation out.