Have you noticed any changes in your skin texture?
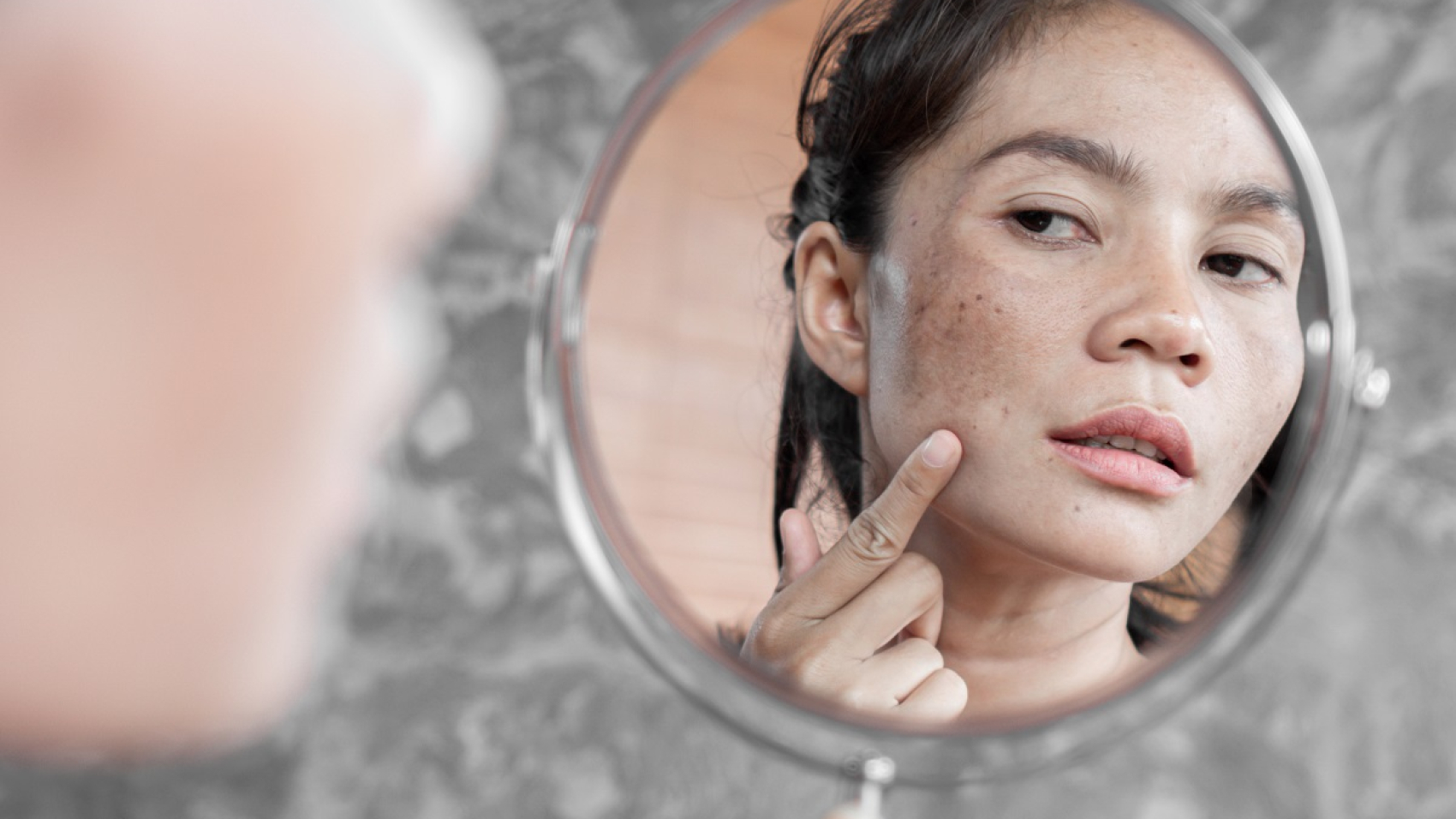
More often than not, you may be asking “What are these spots?” and “Why is it happening?” every time you looked into the mirror.
Let me share it with you. The spots that you see on your skin surface are called pigmentation. We are here to share more info about this skin condition and help you to fix it.
Let’s read more to find out.
So, what exactly is pigmentation?
Pigmentation refers to a skin condition in which patches of skin become darker in color caused by the accumulation of melanin on the skin.
Pigmentation can also be caused by genetics or a variety of factors that interfere with melanin production, allowing skin color to appear unusual.
Melanin is produced by melanocytes and acts as a miniature umbrella to protect skin cells from sun and UV damage.
The pigmentation that occurs on our skin differs. There are several common types of pigmentation that can be found on the surface of our skin.
Types of Pigmentation
#1 Age Spots
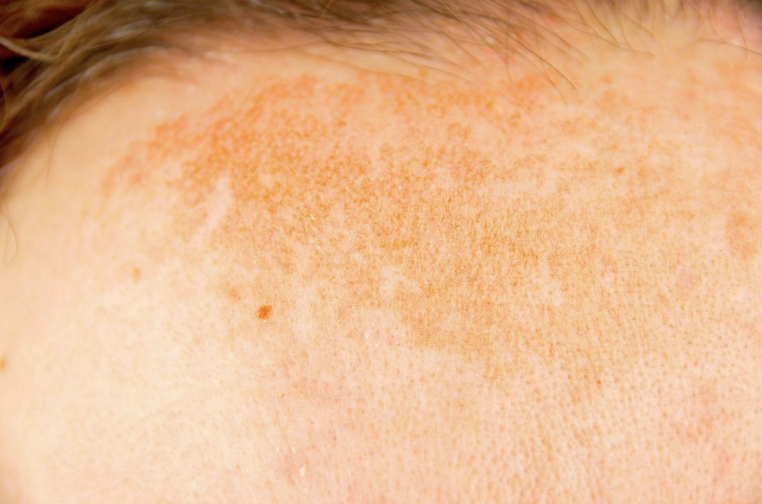
WHAT – They are known as liver spots, and they usually appear on the face after the age of 40, implying that the skin has begun to age. Age spots are normally oval in shape, vary in size, and are tan, brown, or black in color.
WHERE – Typically found on sun-exposed areas, especially the cheekbones.
CAUSES
- Overexposure to Sun – Melanin accumulates on skin areas that have been exposed to UV rays. Countries near the equator like Singapore experience yearlong UV exposure. According to dermatologists, frequent tanning salon visits can also contribute to the development of age spots.
- Aging – Adults over the age of 50 are more prone to developing age spots. Age spots are most common in people who spend a lot of time in the sun, especially during outdoor activities.
#2 Melasma
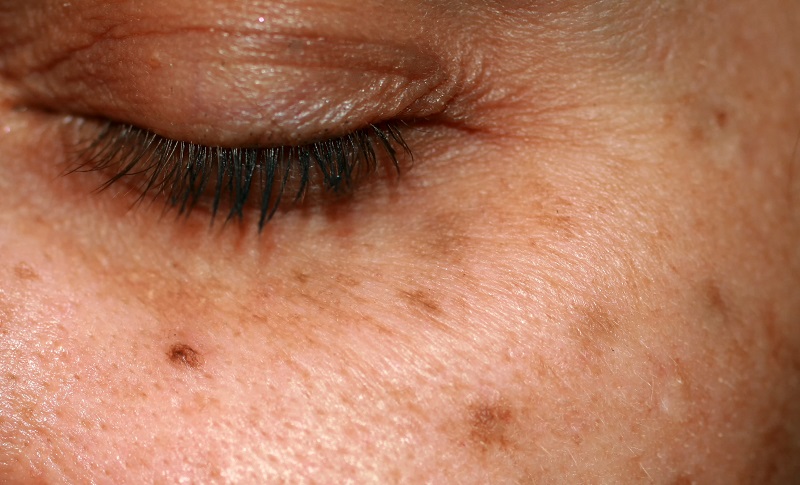
WHAT – A type of dark spot that is more common in people with darker skin tones and is distinguished by a butterfly-shaped mark.
Melasma is also known as chloasma. It is typically characterized by patchy brown discoloration that spreads across specific areas of the face, giving the skin a dull appearance.
WHERE– Melasma on the face is most commonly seen across the upper cheeks. Nevertheless, other areas of the face, such as the forehead, upper lip, and chin, may also be affected.
CAUSES
- Genetics – If there is a known family history of melasma, one is at a higher risk of developing it.
- Pregnancy – UVA and UVB rays can stimulate the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for the majority of pigmentation issues. According to a study, about 50–70% of pregnant women are said to be affected by melasma, a type of pigmentation problem caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light during pregnancy.
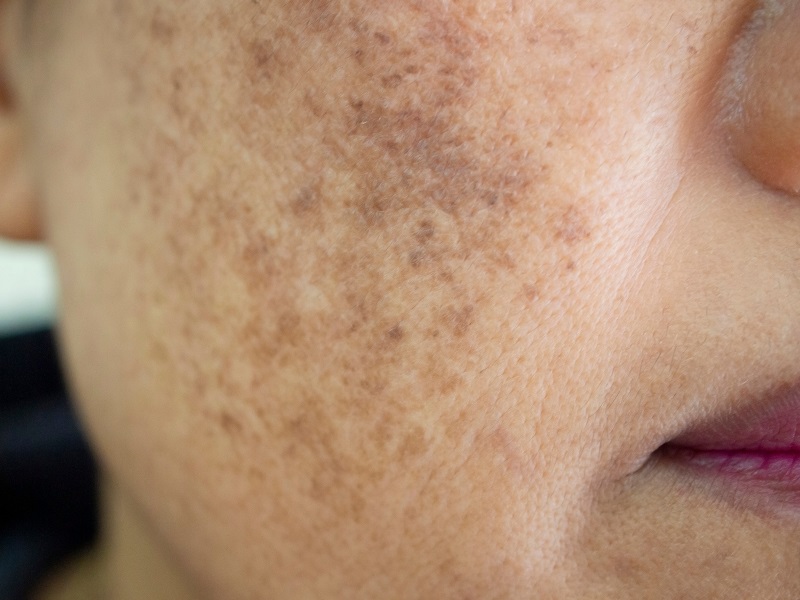
#3 Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
WHAT– One of the most common pigmentation problems in people with Asian skin. It is usually tan, brown, or black in color and develops from inflamed injuries. These can be difficult to cure when a deeper skin layer is involved.
WHERE– This is caused by facial injuries. These wounds can result from razor cuts, burns, or even infected zits from squeezing.
CAUSE
- Inflammation or injury to the skin.
#4 Post-Acne
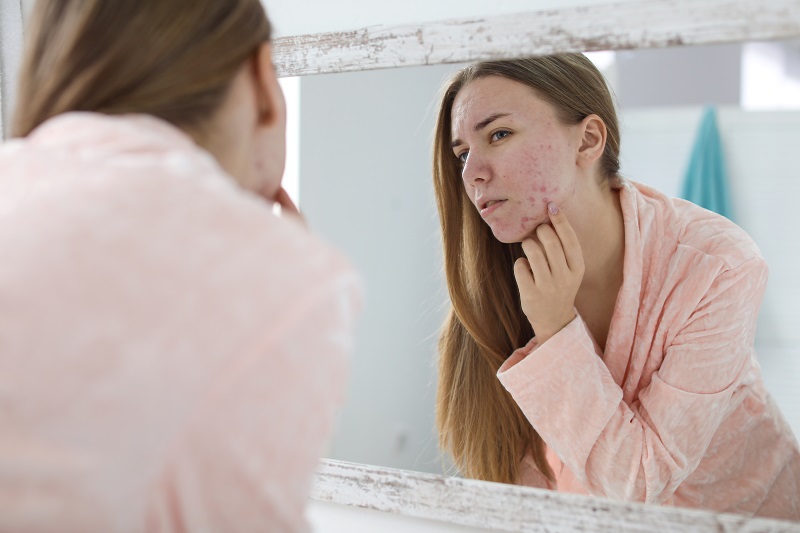

WHAT – Reddish and dark in color spots on the skin and usually developed from the healing of acne wounds.
WHERE – It often appears on areas of the skin that is prone to pimple breakouts.
CAUSES
- Use of unsuitable skin products – Acne may worsen with the use of overly drying facial cleansers and alcohol-based products. Aside from that, skincare products for acne-prone skin may be too harsh for the skin. When used excessively, the skin may be drier, causing it to create even more oil.
- Pimples squeezing – When the extraction is not done properly, the skin and tissue beneath it may be damaged, increasing the chances of wound infection.
Types of Treatment to Remove Pigmentation
It is perfectly normal to have pigmented skin. However, there are always ways for us to fix our pigmented skin. These are the two treatments that you can try:
i) Home Remedies
You only need one of these items for home remedies, and you are ready to go!
- Extract from green tea
- Aloe Vera gel
- Apple cider vinegar
- Red Onion
If you already have one of these, all you have to do is apply one of the items to the pigmented area of your skin for 15 minutes every day. You will be able to feel and see the results after two weeks. Trust me, I am sure you will be surprised at how well these items help your skin recover.
ii) Professional Medical Treatment
There are several treatments available in Singapore to remove pigmented skin. Among the treatments are:
- Facial treatments which normally tailored to the intensity of the pigmentation issue while taking the individual’s skin type into consideration. Depending on the pigmented skin condition, this type of treatment may cost $50 to $300 per session.
- Laser peel treatments which reduce the pigmentation in our skin by using targeted light beams. The treatment, which normally costs $150 per session, can be completed in as little as 15 minutes, depending on the treatment area.
- Microdermabrasion treatments which use a minimally abrasive tool to rejuvenate the skin and replenish the overall tone and texture of the skin. The cost of this treatment usually varies from $80 to $250 per session, depending on the state of the pigmented skin.
- Chemical peels perform by exfoliating the top layer of the skin, as well as the dark spots, with glycolic acid and salicylic acid, accelerating the skin lightening process. This type of treatment can cost between $128 and $238 per session.
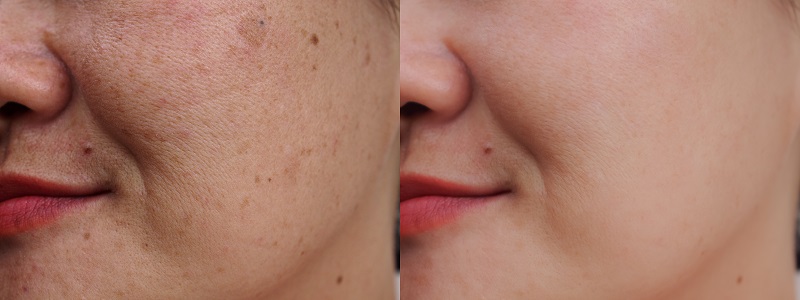
It is important to note that all of the treatments listed above are always performed by a professional dermatologist. All of the treatments tend to have the same post-effect treatment such as redness in the treated skin area.
But do not worry! The redness will go away in a few days.
In short, pigmentation can be fixed by a few remedies as listed in the article, and a proper skincare regime.